- Home
- Shop
- Blog & News
- How to become an instructor?
- Instructor Resources
- Knowledge Base
- Instructing skills
- Need a RYA Instructor or Trainer?
Tidal Anomalies:

If you were to look at a seemingly 'simple' area such as the English Channel, Tidal streams flow one way and then the other, therefore 'in theory' at a Nodal Point the Tidal height remains constant. However this would only be the case if there were no physical features, restrictions in channel widths, harbours or varied depths then this would be the case, which we know it is not.
Due to the water friction caused by the varied depths, channel widths, land features etc the tide is distorted. The areas around Nodal Points can therefore have Double HW's or Double LW's.

Poole Harbour's Tidal Anomaly:
An example of an area where this is very apparent is Poole, Dorset which has double HW. Poole Harbour is both close to a Nodal Point but also a standing wave located in the English Channel which causes this. It also means the tidal stream at Poole Harbour entrance ebbs and flows 8 x a day (rather than x 4 like most other areas).
Though the tidal range is relatively small in Poole Harbour (Neap = 0.4m / Spring = 1.5m) it also has to run in and out of a fairly small gap at Poole Harbour entrance which in turn creates strong tidal streams at that location.
For comparison purposes.. a 'normal' tidal curve (in this example at Worthing) the tide rises and falls evenly every 6 hours. Whereas in Poole Harbour the tide rises to HW, falls marginally, then rises again marginally to create a 2nd HW then falls to LW
Tidal Curve - Worthing, UK

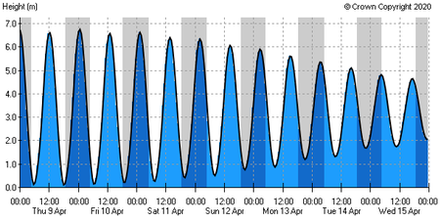
Tidal Curve - Poole Harbour, UK


Mediterranean Tides:

Firstly, yes, the Mediterranean does have tides though generally of fairly irrelevant sizes when boating.
The tides are limited as the Med is almost landlocked with the inlet from the Atlantic Ocean being fairly small therefore making it almost a huge lake ! Dependant on where you look depends on the information you will gather about the maximum Tidal Range in the Med, but the Maximum Mean Variation seems to be approx 40cm but more often 10 - 15cm (obviously these ranges also fluctuate according to the weather, atmospheric conditions etc).
Looking at Palma de Mallorca, Spain as an example you can see the Tidal range is maximum 20cm in these illustrations:
Neaps:

Springs:

Tide Glossary of Terms:
- Tidal Node (Amphidrimic Point) - a geographic location which has zero tide.
- Chart Datum - water depths that are displayed on a nautical chart such as Lowest Astronomical Tide (L.A.T.)
- Current - a horizotonal movement of water
- Double Tide - A double headed tide i.e. a Double High Tide = High Water consisting of two HW's of nearly the same height seperated by a small depression. Double Low Tide = Low Water consisting of two LW's seperated by a small elevation.
- Ebb - Tidal current moving away from a shore / into a harbour/river etc
- Eddy - a circular movement of water in a relatively small area.
- Equinoctial Tides - Tides occurring near the time of an equinox
- Flood - Tidal current moving towards a shore / into a harbour/ river etc
- Flow - Combination of Tidal Stream & Current
- High Water (H.W.) / High Tide - The maximum height reached by a rising Tide.
- High Water Mark - the mark / line left on the shore once the High tide has retreated.
- Knot - a speed unit for the nautical mile per hour
- Low Water (L.W.) / Low Tide - The minimum height reached by a falling tide.
- Lower High Water (LHW) - the lowest of the high waters of any day
- Lowest Astronomical Tide (L.A.T.) - The lowest tide level that can be predicated to occur.
- Mean High Water (MHW) - a tidal datum which is the average of all the high waters.
- Mean Low Water (MLW) - a tidal datum which is the average of all the low waters
- Mean Range - The difference between MHW and MLW
- Neap Tides - Tides of decreased range / currents that occur twice month when the moon is at 90 degrees to the earth / you see a 1/4 moon.
- Nodal Point - The zero or near zero tide point in an amphidromic region
- Range - Difference between HW and LW
- Race - a very rapid current through a narrow channel
- Rip - Agitation of water caused by the meeting of currents.
- Slack Water - when the tidal current's speed is zero or near zero
- Spring Tide - A tide that occurs just after a new or full moon with the greatest difference between HW & LW
- Stand - Interval at HW or LW when there is not much change in the height of tide.
- Standing Wave - A wave that oscillates without progressing
- Tide Rip - Rapid current over an irregular sea bed.
- Tide Table - Tables which give daily predictions of the heights of HW's and LW's
