- Home
- Shop
- Blog & News
- How to become an instructor?
- Instructor Resources
- Knowledge Base
- Instructing skills
- Need a RYA Instructor or Trainer?
Synoptic Charts:

Synoptic = summary of current situation.

A = Isobar
B = Warm Front
C = Cold Front
D = Pressure in Millibars
E = Occluded Front
F = Trough
G = Low Pressure System
H = High Pressure System
Isobars:

What do isobars tell us?
Wind Speed:
- Closely spaced Isobars indicate large pressure changes causing wind speeds to increase.
Wind Direction:
In the Northern Hemisphere Winds will:
- Winds will blow anti-clockwise around an area of Low Pressure (Cyclone)
- Winds will blow clockwise around an area of High Pressure (Anti-Cyclone)
Pressure:
- Lines of equal atmospheric pressure
Wind Direction (Northern Hemisphere):
Winds will blow anti-clockwise around an area of Low Pressure (Cyclone)

Winds will blow clockwise around an area of High Pressure (Anti-Cyclone)

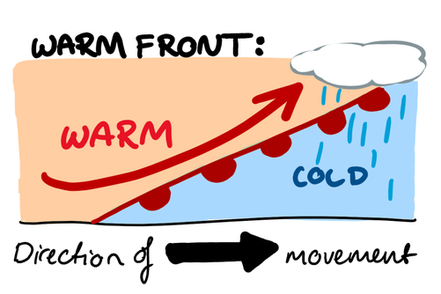
Warm Front:
A warm front occurs when a warm air mass slides over a cold air mass.
These are formed when warm air rises over a mass of cold air. As the air lifts it cools, expands and condenses the water vapour as wide flat clouds. Warm fronts usually bring low and thick cloud & drizzle.

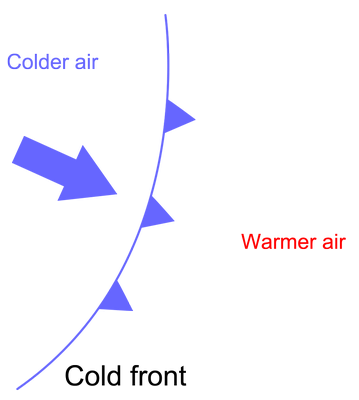
Cold Front:
Usually associated with Depressions. A cold front is a transition zone where a cold air mass is replacing a warmer air mass. The cold air is following the warm air and gradually moves underneath the warmer air.
Commonly, when the cold front is passing, winds become gusty; there is a sudden drop in temperature, and heavy rain, sometimes with hail, thunder, and lightning. Lifted warm air ahead of the front produces cumulusor cumulonimbus clouds and thunderstorms.

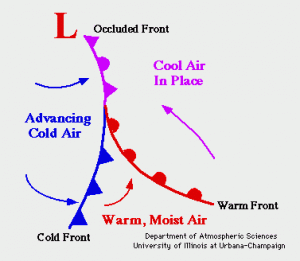
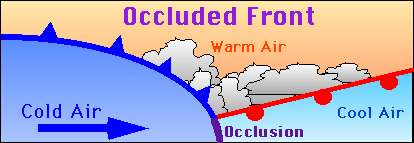
Occluded Front
This occurs where two different air masses meet. A band of thick cloud is created when the cold air catches up with the warm front.
Occluded fronts usually bring sudden downpours of heavy rain.
Trough:
trough is an elongated (extended) region of relatively low atmospheric pressure, often associated with fronts. Most troughs bring clouds, showers, and a wind shift, particularly following the passage of the trough. This results from convergence or "squeezing" which forces lifting of moist air behind the trough line.

